One of the most common treatment recommendations for urinary incontinence includes exercising the muscles of the pelvis. These exercises strengthens pelvic floor muscles and sphincter muscles to reduce stress leakage. Patients younger than 60 years old benefit the most. The patient should do at least 24 daily contractions for at least 6 weeks.It is possible to assess pelvic floor muscle strength using a Kegel perineometer
Increasingly there is evidence of the effectiveness of pelvic floor muscle exercise (PFME) to improve bladder control. For example, urinary incontinence following childbirth can be improved by performing incontinence exercises. Begin incontinence exercises with empty bladder. Start with gravity assisted positioning(hips higher than the heart such as supported bridge or elbows/knees position)
CONTRACT-RELAX TECHNIQUE: Instruct to tighten the pelvic floor muscles as if attempting to stop urine flow or hold back gas. Hold for 3 to 5 seconds and relax for at least the same length of time. Repeat up to 10 times. Watch the patient to encourage normal breathing pattern.
QUICK CONTRACTIONS: Repeat contractions of pelvic floor muscles while maintaining a normal breathing rate and keeping accessory muscles relaxed. Try for 15 to 20 repetitions per set with coughing and sneezing
ELEVATOR EXERCISES: Instruct the patient to imagine riding in an elevator. As the elevator goes up from one floor to next, contracts the pelvic floor muscles a little more. As strength and awareness improves, add more floors to the sequence of the contraction. Instruct the patient to relax the muscles as if descending one floor at a time.
Studies also report that 50 – 75% of patients who perform only incontinence exercise have a substantial improvement in their symptoms, including elderly people who have had the problem for years. Incontinence exercises may be especially helpful for women in their 40s and 50s who suffer from stress incontinence.
Pelvic Floor Muscle (Kegel) Exercises/Incontinence exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor that support the bladder and close the sphincters. The general approach for learning and practicing incontinence exercises is as follows:
- Since the muscles are sometimes difficult to isolate, the best method is to first learn while urinating. The patient begins to urinate and then contracts the muscle in the pelvic area with intention of slowing or stopping the flow of urine. Women should contract the vaginal muscles as well. They can detect this by inserting a finger inside the vagina. When the vaginal walls tighten, the pelvic muscles are being correctly contracted. Patients should place their hands on their abdomen, thighs, and buttocks to make sure there is no movement in these areas while exercising.
- An alternate approach is to isolate the muscles used in Kegel contractions by sensing then squeezing and lifting the muscles in the rectum that are used in passing gas. (Again, women should contract the vaginal muscles as well.)The first method is used for strengthening the pelvic floor muscles. The patient slowly contracts and lifts the muscles and holds for 5 seconds, then releases them. There is a rest of 10 seconds between contractions.
- The second method is simply a quick contraction and release. The object of incontinence exercises is to learn to shut off the urine flow rapidly.
- In general, patients should perform 5 – 15 contractions, three to five times daily.
Caution
- Once learned, incontinence exercises should not be performed while urinating more than about twice a month, since this practice may eventually weaken the muscles.
- In women, incorrect or overly vigorous exercises may cause vaginal muscles to tighten excessively, resulting in pain during sexual intercourse.
- Overexercise can tire muscles and cause more leakage.
- Incontinence will return to its original severity if these exercises are discontinued.
Bladder Training
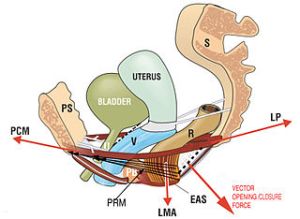
Bladder training involves a specific and graduated schedule for increasing the time between urinations:
- Patients start by planning short intervals between urinations, then gradually progressing with a goal of voiding every 3 – 4 hours.
- If the urge to urinate arises between scheduled voidings, patients should remain in place until the urge subsides. At the time, the patient moves slowly to a bathroom.
- Incontinence exercises(called Kegel exercises) may help control urine leakage. Incontinence exercises improve the strength and function of the urethral sphincter.
Some women may use a device called a vaginal cone along with incontinence exercises. The cone is placed into the vagina, and the woman tries to contract the pelvic floor muscles in an effort to hold it in place. The device may be worn for up to 15 minutes. This procedure should be done two times a day. Within 4 – 6 weeks, most women have some improvement in their symptoms.
Types of urinary incontinence
There are 5 types of urinary incontinence.
- Stress incontinence Stress incontinence is when urine leaks because of sudden pressure on your lower stomach muscles, such as when you cough, laugh, lift something or exercise. Stress incontinence usually occurs when the pelvic muscles are weakened, for example by childbirth or surgery. Stress incontinence is common in women.
- Urge incontinence This occurs when the need to urinate comes on very suddenly, often before you can get to a toilet. Your body may only give you a warning of a few seconds to minutes before you urinate. Urge incontinence is most common in the elderly and may be a sign of a urinary tract infection or an overactive bladder.
- Overflow incontinence This type of incontinence is the uncontrollable leakage of small amounts of urine. It’s caused by an overfilled bladder. You may feel like you can’t empty your bladder all the way and you may strain when urinating. This often occurs in men and can be caused by something blocking the urinary flow, such as an enlarged prostate gland or tumor. Diabetes or certain medicines may also cause the problem.
- Functional incontinence This type occurs when you have normal urine control but have trouble getting to the bathroom in time. You may not be able to get to the bathroom because of arthritis or other diseases that make it hard to move around.
- Mixed incontinence This type involves more than one of the types of incontinence listed above.
URINARY INCONTINENCE TREATMENT
Treatment depends on how severe the symptoms are and how much they interfere with your everyday life. The doctor may ask that you stop smoking (if you smoke) and avoid caffeinated beverages (such as soda) and alcohol. You may be asked to keep a urinary diary, recording how many times you urinate during the day and night, and how often urinary leaking occurs.
There are four major categories of treatment for stress incontinence:
- Behavioral changes
- Incontinence exercises
- Medication (not describe)
- Surgery (not describe)
Behaviour Changes
Examples of behaviour changes include:
- Decreasing any excessive fluid intake (you should not decrease your fluid intake if you drink normal amounts of fluid)
- Urinating more frequently to decrease the amount of urine that leaks
- Regulating bowel movements with dietary fiber or laxatives to avoid constipation (which can worsen incontinence)
- Quitting smoking to reduce coughing and bladder irritation (and your risk of bladder cancer)
- Avoiding alcohol and caffeine, which can overstimulate the bladder
- Losing weight if you are overweight
- Avoiding food and drinks that irritate the bladder, such as spicy foods, carbonated beverages, and citrus
- Keeping blood sugar under control if you have diabetes
PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING: It includes incontinence exercise or kegel exercises
The aim of incontinence exercises is to improve muscle tone by strengthening the pubococcygeus muscles of the pelvic floor. Kegel is a popular prescribed exercise for pregnant women to prepare the pelvic floor for physiological stresses of the later stages of pregnancy and vaginal childbirth. Incontinence exercises are said to be good for treating vaginal prolapse and preventing uterine prolapse in women and for treating prostate pain and swelling resulting from benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostatitis in men. Incontinence exercises may be beneficial in treating urinary incontinence in both men and women. Incontinence exercises may also increase sexual gratification and aid in reducing premature ejaculation.
Kegel exerciser:
A Kegel exerciser is a medical device designed to be used by women to exercise the pubococcygeus muscle (also called the PC muscle). There are three main types: barbells, springs, and rubber bulbs. Made of smooth, polished solid stainless steel, it is cylindrical in shape, with a rounded bulge at each end. They typically weigh one pound (454g) and measure approximately 6¾ inches (17.1 cm) in length with a diameter of one inch (2.5 cm) at the widest part. Being made of stainless steel, vaginal barbells are nonporous and can be wiped clean with a cloth moistened with mild soap and water.
Spring devices are made of plastic, with removable springs to allow progressive resistance. These allow pressing directly against resistance. An advantage of rubber bulb devices is that they provide visual feedback (via a gauge) of how much pressure is being applied.
Electrical stimulation:
Brief doses of electrical stimulation can strengthen muscles in the lower pelvis in a way similar to exercising the muscles. Electrodes are temporarily placed in the vagina or rectum to stimulate nearby muscles. This can stabilize overactive muscles and stimulate contraction of urethral muscles.
Biofeedback:
Biofeedback uses measuring devices to help the patient become aware of his or her body’s functioning. By using electronic devices or diaries to track when the bladder and urethral muscles contract, the patient can gain control over these muscles.
Treatment sessions usually last 20 minutes and may be done every 1 – 4 days. Newer techniques are being investigated, including one that uses a specially designed electromagnetic chair that causes the pelvic floor muscles to contract when the patient is seated
 ⠀
⠀ ⠀
⠀